4 Things Industry 4.0 – Sand Batteries, Self-Swapping Robots & Strategy Shifts: Inside the Next Wave of Industrial Evolution

Presented by

Happy July 28th, tech tamers and data wranglers!
While most people are trying to beat the heat, the world of Industry 4.0 is busy turning it into battery power—literally. Finland's heating homes with sand, China’s robots are changing their own batteries like they just got opposable thumbs, and the U.S. is fast-tracking data centers with all the subtlety of a freight train. Oh, and Intel? They're trimming the fat and handing every chip decision straight to the CEO—because why not?
In this week’s Learning Lens, a Rust-powered storage engine ditches hard drives for object storage and cloud-native swagger. And in Byte-Sized Brilliance, we reflect on a time when 5MB came with a forklift and a forklift operator.
Let’s dive in before the robots start writing this thing themselves.
New U.S. AI Strategy Boosts Data Center Expansion, Reduces Environment Oversight

President Trump’s recently announced AI Action Plan directs federal agencies to accelerate construction of energy-intensive data centers by softening air and water quality regulations and streamlining permitting processes to support expanded electricity generation. The initiative aligns with priorities for "American energy dominance" by favoring fossil fuel sources—primarily natural gas and coal—to meet increased power demand. While major tech firms plan to secure nuclear energy supplies, concerns persist that, without significant investment in renewables, the expansion may drive higher emissions and consumer electricity costs.
PepsiCo Ends Manufacturing at Detroit Beverage Facility After Eight Decades

PepsiCo announced it will cease manufacturing, transport, and maintenance operations at its Detroit plant on Mack Avenue as of September 27, 2025, affecting approximately 83–84 employees. While production will end, warehouse, delivery, sales, fleet, and field service functions will remain active at the site. The company said it will offer pay and benefits to affected staff during the transition and aims to support redeployment where possible. The decision follows prior closures of PepsiCo facilities in Chicago, Cincinnati, Atlanta, and Harrisburg in 2024, and is part of an effort to integrate its North American snack and beverage divisions, reduce costs, and respond to declining domestic beverage demand.
Walker S2 Enables True 24/7 Factory Autonomy with Self‑Battery Swap
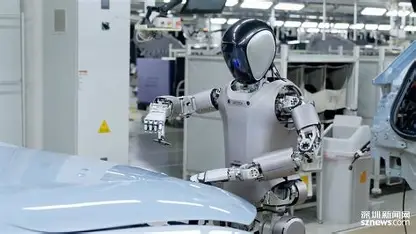
Chinese robotics firm UBTECH has unveiled the Walker S2 humanoid robot, the first in the world capable of autonomously swapping its own battery without human intervention. The robot employs a dual-battery system allowing continuous operation, approximately two hours of walking or four hours of idle time per battery—and can perform a full battery exchange at a dedicated station in under three minutes. Walker S2 monitors its power levels, determines when to replace or recharge, navigates to the recharging station, and uses its arms to remove a depleted pack and install a fresh one, all while remaining operational. The innovation removes the downtime typical of charging cycles, enabling uninterrupted industrial deployment and marking a significant advancement in autonomous robotics for manufacturing and automation environments.
Sponsor Message

Who Uses WinCC OA?
WinCC OA – An IIoT Platform Built for Engineers, Backed by Engineers
Trusted by Engineers Worldwide: Why Choose WinCC OA
WinCC OA: The Platform Engineers Rely On
From energy grids to smart cities, WinCC OA is powering the systems that keep the world running. But what truly sets it apart? The engineers behind the projects—and their stories.
WinCC OA isn’t just a SCADA system. It’s a flexible, future-ready IIoT platform trusted by professionals who need more than just monitoring—they need control, customization, and confidence.
Here’s what real users say:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLMoKkI_Hd2R0y8-1v_J8QOkDsCqwNARg8
Used Across Industries:
Energy & Utilities – Grid control, renewables, and smart metering
Infrastructure – Metro systems, tunnels, airports
Manufacturing – From discrete to process industries
Smart Cities – Urban automation and data integration
Research & Development – Labs and testbeds for innovation
Whether you're building a new IIoT architecture or modernizing legacy systems, WinCC OA is the platform engineers trust to get the job done—on their terms.
Hyper links:
Request your free WinCC OA Evaluation License now!
World’s Largest Sand‑Battery Now Powers Finnish Heating Network

A 1 MW/100 MWh industrial-scale sand battery developed by Polar Night Energy is now operational in Pornainen, southern Finland, serving as the primary heat source for the local district heating network managed by Loviisan Lämpö. The cylindrical silo (approximately 13 m tall and 15 m wide) contains around 2,000 tons of crushed soapstone which stores renewable energy as high-temperature heat. It can supply nearly a month’s worth of summer heat demand and up to a week in winter. The installation is expected to reduce CO₂-equivalent emissions from local heating by about 160 tons annually—nearly a 70 percent decrease—while eliminating oil usage and cutting wood-chip consumption by roughly 60 percent The project is viewed as a scalable model for decarbonizing district heating and advancing the circular economy, with further international deployments in planning.
Industry 4.0 Highlights
Intel Overhauls Strategy Under CEO Tan, Emphasizes Discipline and Core Focus
Intel CEO Lip-Bu Tan has announced a sweeping restructuring: the company will reduce its workforce from around 99,500 to approximately 75,000 employees—at least a 15–22% cut—through layoffs and attrition by end-2025. Expansion projects in Germany, Poland, and Ohio are being delayed or cancelled, and some production is being shifted from Costa Rica to Vietnam and Malaysia to optimize cost control. Tan criticized past strategy as "unwise and excessive," stressing a new demand-driven investment model: advancing Intel 14A technology only if significant customers commit, while focusing on ramping 18A chips throughout the next several years. He also plans to spin off Intel’s Network & Edge (NEX) division and divest non-core assets, while increasing direct executive oversight of AI and chip design decisions; every major chip rollout now requires his approval. Despite recent restructuring costs—including a $2.9 billion Q2 net loss—Intel exceeded revenue expectations ($12.9 b vs. $11.9 b forecast) and projects continued revenue growth in Q3, lending short-term support to Tan’s turnaround plan.
Charge Robotics Introduces Portable Robot-Driven Factories for Solar Installation
Charge Robotics, an MIT alumnus‑led startup founded in 2021, has deployed Sunrise, a portable factory system that automates nearly all steps of utility‑scale solar farm installation on-site. The system is shipped to solar project sites where components—such as tracks, mounting brackets, and solar panels—are fed into robotic assembly lines. Those lines build 40‑foot "solar bays" (~800 lb), which an autonomous vehicle then positions in place. With only the initial ground stake driving done manually, the system handles assembly, quality control via vision systems, and installation, significantly reducing labor needs and accelerating construction timelines. After a successful pilot with SOLV Energy, which demonstrated feasibility, the startup has secured $22 million in funding to launch commercial deployments later in 2025.
Learning Lens

Accelerating Cloud-Native Storage with SlateDB
SlateDB is an embedded key-value storage engine built in Rust, designed specifically for cloud-native applications. Unlike traditional LSM-tree systems, SlateDB writes data directly to object storage such as S3, GCS, or MinIO—eliminating the need for local disks and offering effectively endless storage capacity with high durability and built-in replication. It employs techniques like batching writes from memtables to object storage as SST files, as well as in-memory and disk caching, compression, bloom filters, and snapshot isolation to manage latency and cost. SlateDB supports ACID-compliant transactions, allows a single writer with multiple reader processes, and enables clones and checkpoints.
👉 Learn more: https://github.com/slatedb/slatedb
Byte-Sized Brilliance
IBM’s First Hard Drive Was the Size of Two Elephants
In 1956, IBM launched the first commercial hard drive—the IBM 305 RAMAC. It stored just 5 megabytes of data and weighed over 2,000 pounds. That’s about the size and weight of two adult elephants… to hold a single MP3. Today, you can fit more than 6 million times that storage on a microSD card the size of your fingernail—and still lose it in your couch cushions.
We Value your Feedback.
Click on the link below to provide us with your thoughts.
|
|
|
|
|
|



Responses